How to Prevent Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
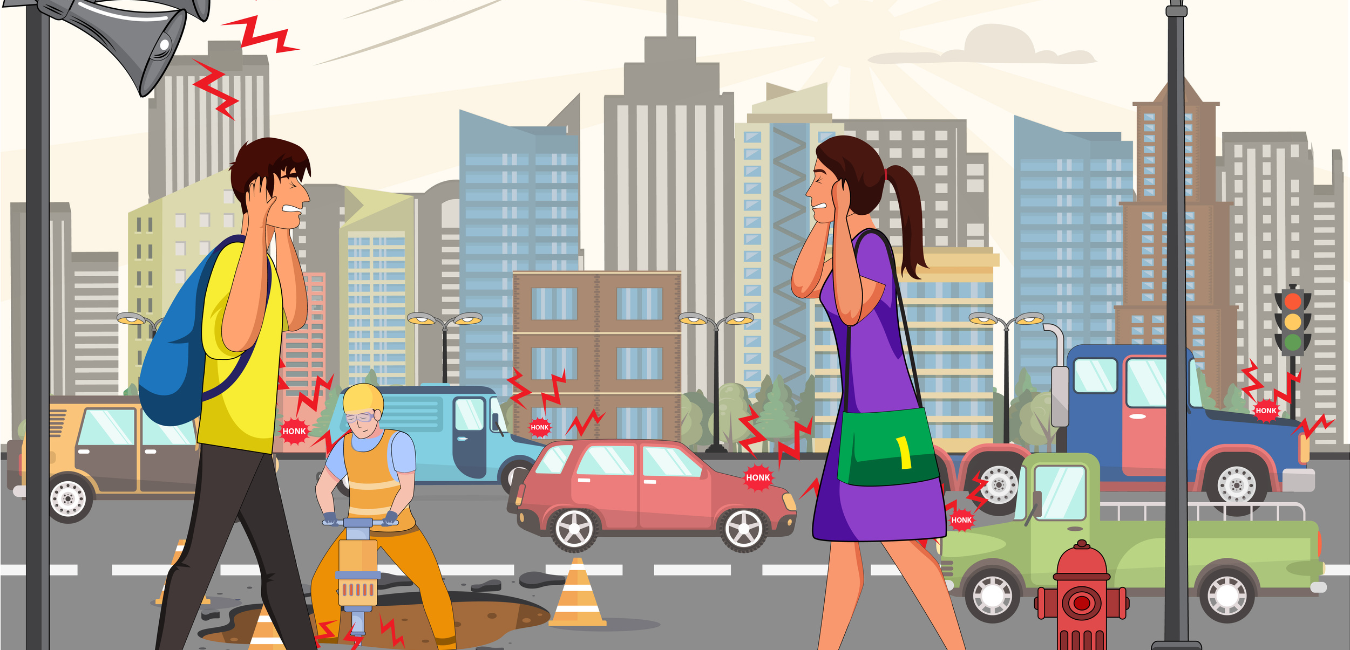
When we are younger, we don’t always consider loud noise’s impact on our hearing. We regularly subject ourselves to loud noises like rock concerts, cranking up music volume, sporting events, and using power tools. However, repeated exposure to these noises can lead to noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) and require medical treatment.
Loud sounds damage sensitive areas in the ear, resulting in ringing/buzzing (tinnitus), hearing loss, communication interference, sleep/concentration disturbances, and sound sensitivity (hyperacusis).
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Causes
Sound is essential to our daily lives, and exposure to it is inevitable. However, prolonged exposure to loud noises can lead to permanent hearing loss.
While some instances of hearing loss may be temporary, such as when your hearing worsens after a particularly loud concert, excessive noise exposure can cause permanent damage, especially when it’s repeated.
While your hearing will likely recover after your first or second concert, you may be setting yourself up to experience permanent damage later in life. The more instances where you’re exposed to excessive noise, the more likely you are to experience lasting effects.
Some sources of excessive noise include:
- Music, stereos, television, movies, and concerts
- Air, land, and water vehicles (trains, buses, trucks, boats, and airplanes)
- Machinery, factories, and power tools
- Animals and people
Prolonged or repeated exposure to loud noises can damage various parts of our ears, including membranes, hair cells, cochlea, and nerves.
How Loud is Too Loud?
Noise that registers above 85 dB can be damaging to your hearing. Often, people are unaware that the noise levels around them have reached damaging levels, especially when they’re exposed to these excessive sounds on a regular basis.
Unfortunately, a number of things we consider normal parts of our everyday lives fall into this category. Anything from listening to music with headphones and going to the movie theatre, to mowing the lawn or using power tools has the potential to damage our hearing.
The more intense the sound, the greater the risk of hearing loss. Louder noises can cause hearing damage in a shorter amount of time, especially if you don’t use hearing protection or take breaks. It’s important to note that hearing loss is caused not only by high noise levels but also by their intensity.
Who Is at Risk?
Everyone is at risk for NIHL. However, the effects of noise-induced hearing loss are especially common among those who work in high-noise environments. Employment with elevated noise levels includes the following industries:
- Machinery
- Mining
- Oil and gas production
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Transportation
- Music
- Teaching
- Dentistry
Occupational hearing loss may have a sudden onset or after years of prolonged exposure. While NIHL is common, it is preventable and if caught in time, the damage can be treatable.
How to Detect Noise Related Hearing Damage
It’s important to note that noise doesn’t always have to be extremely loud to cause damage to your hearing. Even music played at high volumes for extended periods of time, especially through headphones or earplugs, can cause damage.
Hearing damage can also come from impulse noise, which is intense and brief, or from continuous noise, which is lower in intensity but extended over longer periods.
Exposure to impulse noise, like fireworks, gunshots, or jackhammers, can cause permanent damage. Continuous noise has a greater likelihood of causing permanent damage because of its louder and prolonged exposure.
Potential Symptoms for NIHL
Early Signs:
- You are unable to follow conversations if there is background noise.
- You experience tinnitus (ringing, whooshing or buzzing in the ears).
- It seems like others are often mumbling when speaking to you.
Sudden Onset:
- There are noticeable changes to your hearing after loud noise exposure.
- You experience ear pain after exposure.
Long Term Damage
- People comment that you are shouting.
- You have to turn the television volume up extremely high to hear it.
How to Prevent Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
While there are some obvious and easy things you can do to prevent hearing loss, such as adjusting the volume of your music and television or avoiding loud environments, there are some situations, particularly work-related ones, that cannot be avoided.
In such cases, it’s important to be proactive and take measures to protect your hearing.
Adjust the Volume of Your Music/Television
Adjust the volume to a comfortable level when enjoying music or watching television. When using earbuds or headphones, pay close attention to the noise level and limit how long you wear them for.
Limit Your Exposure
If you’re at a public event, such as a concert, you can protect your hearing by limiting your exposure to intense and extremely loud noises. Keeping your distance from the source of the noise or taking breaks will help reduce the potential for long-term damage.
Protect Your Hearing
You can’t always avoid excessive noise, especially if your job involves regular exposure to loud and intense noises. However, when you are in loud environments, wearing protective hearing is essential.
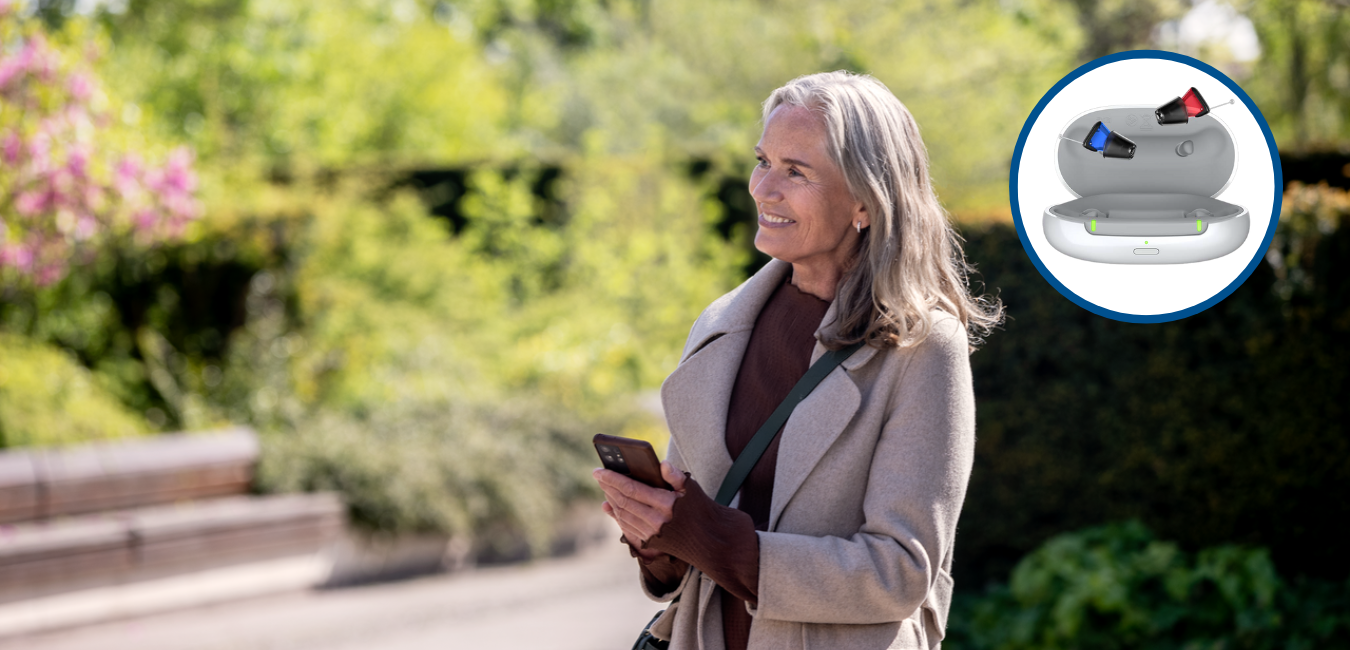
There are a number of earplugs, headphones and noise-cancelling earmuffs available that will help keep your ears safe in excessively noisy environments. No matter what the situation or event is, there is protective hearing gear available to suit your needs.
Just make sure to choose hearing protection that fits you well, as poorly fitting gear won’t be effective. At the same time, hearing protection shouldn’t block out sound completely, as this can be dangerous in certain situations.
Regularly Check Your Hearing
One of your best tools against noise-induced hearing loss is regular hearing check-ups. Visiting a hearing specialist and having your hearing checked is the best way to detect the symptoms of NIHL early on, which will give you the best chance of reducing damage and treating it.
These checks are critical if you are at risk of occupational hearing loss, and work in a particularly noisy environment. However, even if you believe your chances of experiencing noise-related hearing damage are minimal, regular hearing checks are still important.
You are likely exposed to damaging levels of noise more frequently than you realize, and without regular checks, the damage may become permanent without you even realizing it.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Treatment and Prevention: How Hearing Solutions Can Help
To prevent noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL), we all need to be aware of the sources of loud noise such as music, machinery, and vehicles, and take proactive measures to protect our hearing. Adjusting the volume of our music and television, limiting our exposure to loud noises, and using hearing protection can help reduce the risk of NIHL. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and taking care of our hearing is essential to our overall well-being.
Start taking charge of your hearing health today with our online hearing test. If you’re concerned you may be experiencing symptoms of hearing damage, you can go here to book an appointment and have your hearing tested by one of our specialists.
References:
(2022, June 7). Could Dad Have Noise Induced Hearing Loss? Hearing Solutions.
https://www.hearingsolutions.ca/could-dad-have-noise-induced-hearing-loss/
(2022, November 3). Loud Noise Can Cause Hearing Loss. Centers for Disease Control
and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/hearing_loss/default.html
Health Canada (2023, June 5). Noise and your health. Government. of Canada.
https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/noise-your-health.htmlHealth
Seelisch, A. (2021, September 1). What You Need to Know About Noise Induced
Hearing Loss. Hearing Solutions. https://www.hearingsolutions.ca/what-you-need-to-know-about-noise-induced-hearing-loss/